What Is a Sitemap?
A sitemap is a file that reveals the construction of your web site, together with its pages and content material. And the relationships between them.
One kind is meant to assist serps crawl your website extra effectively. One other kind is meant to assist customers higher navigate your web site.
Why Do You Want a Web site Sitemap?
The bigger and extra complicated your web site is, the harder it may be for each customers and serps to navigate. However sitemaps make it simpler.
All this implies sitemaps are necessary. As a result of they’ll result in:
- Higher discoverability: An XML sitemap (extra on this within the subsequent part) helps serps uncover necessary pages in your web site. That is notably useful for big web sites which have hundreds of pages and could also be impacted by a restricted crawl finances.
- Sooner indexation: For newer web sites, submitting an XML sitemap can result in extra pages rating sooner. And for web sites that replace present content material, Google can uncover these adjustments sooner once they’re included within the sitemap.
- Improved person expertise: HTML sitemaps (extra on this within the subsequent part) could make it simpler for customers to search out precisely what content material they’re in search of. As a result of they’re capable of see all of your most necessary pages in a single place.
Totally different sitemaps supply totally different advantages, so let’s focus on these subsequent.
What Are the Totally different Varieties of Web site Sitemaps?
There are two varieties of sitemaps:
- XML sitemaps: Sitemaps written in a particular format designed for search engine crawlers
- HTML sitemaps: Sitemaps that appear to be common pages and assist customers navigate the web site
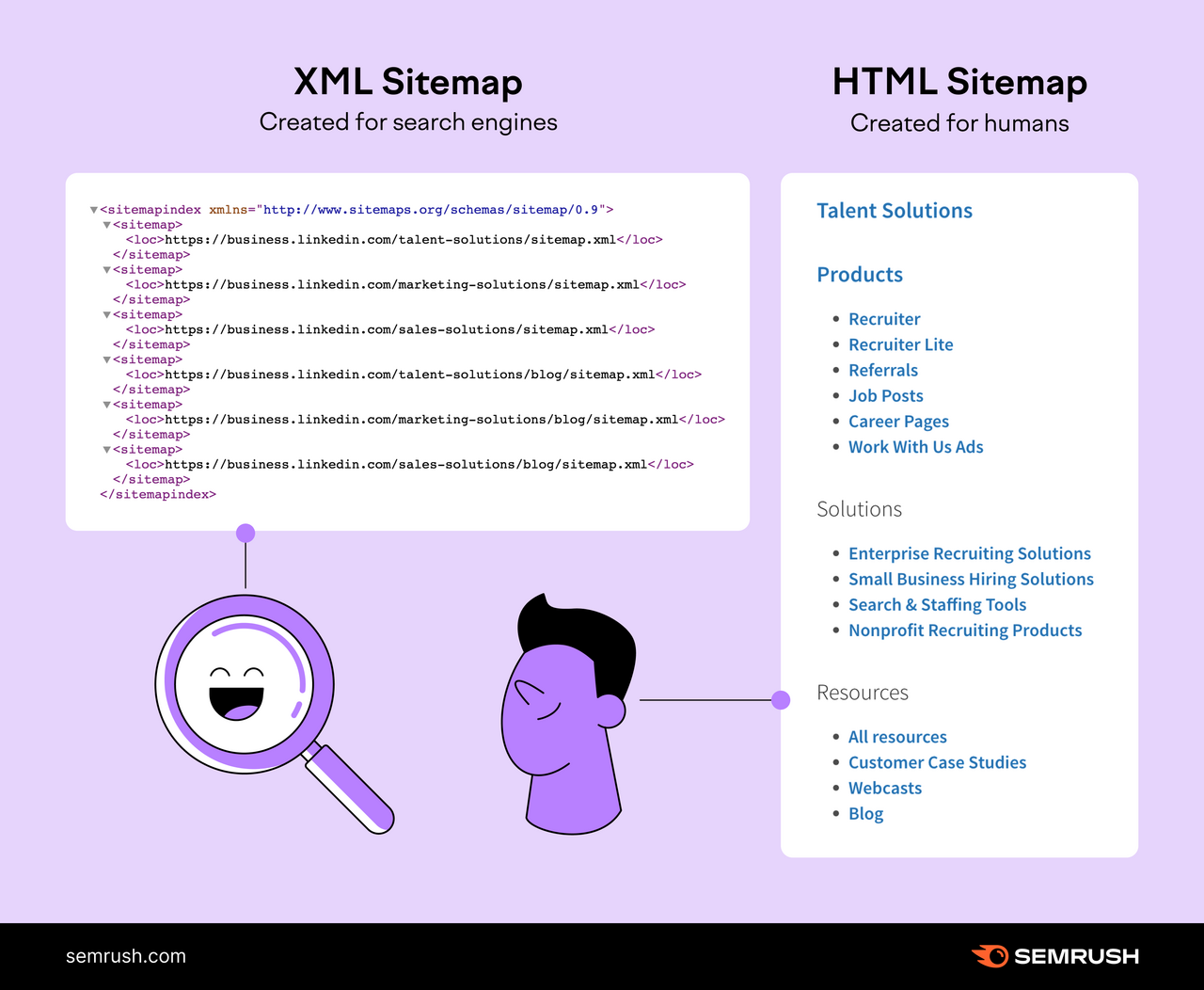
XML Sitemaps
Extensible Markup Language (XML) sitemaps are the popular format for serps like Google.
They supply three major varieties of info to serps:
- The record of all of the URLs you need to have listed
- The “lastmod” attribute that informs when the URLs had been final up to date
- The “hreflang” attribute that reveals native variants of the URLs
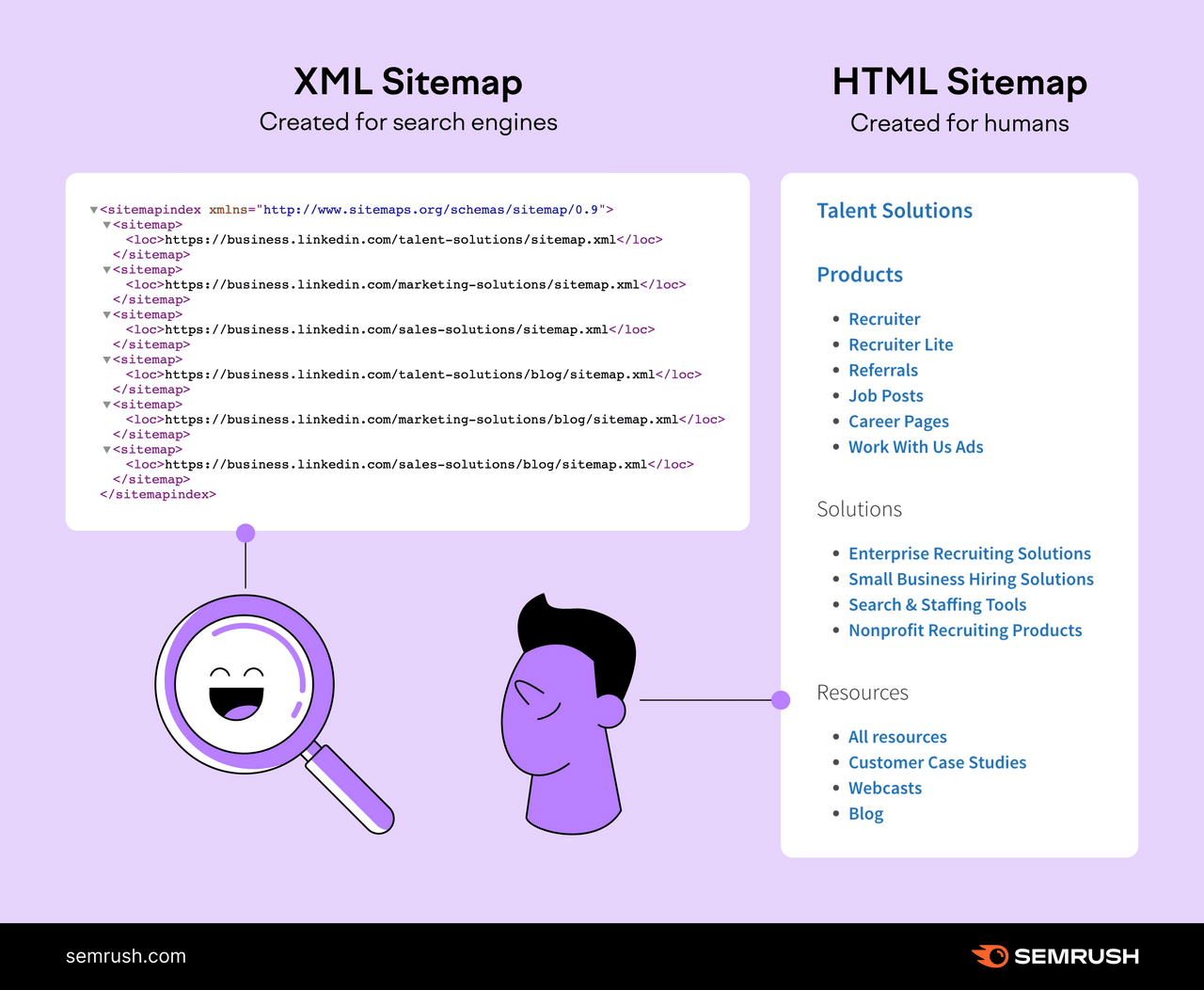
These sitemaps look one thing like this:
Whereas XML sitemaps are particularly appropriate for big web sites, web sites with in depth archives, or new web sites with few hyperlinks, each web site can profit from having one.
Plus, it solely takes a couple of minutes to create one.
Additional studying:
- XML Sitemap: What It Is & How you can Generate One
- WordPress Sitemap: How you can Create, Verify, and Submit One
HTML Sitemaps
HTML sitemaps was once a well-liked method to enhance an internet site’s navigation and supply hyperlinks to all of your necessary pages in a single place.
This is an instance of an HTML sitemap from H&M Group:

As you may see, it’s a typical web page with hyperlinks to numerous pages organized in a hierarchical method.
Though HTML sitemaps aren’t that frequent anymore, some voices within the search engine optimisation group nonetheless say they’re a should. As a result of HTML sitemaps can enhance your inner linking and supply one other layer of navigation for complicated web sites with many pages.
However don’t use an HTML sitemap as a substitute for good website navigation components (comparable to menus, footer hyperlinks, breadcrumbs, classes, and so on.).
Google’s John Mueller spoke to this on Mastodon:
In different phrases, customers shouldn’t want a sitemap to successfully navigate your web site.
How you can Discover a Sitemap
Listed below are some efficient methods to discover a sitemap on an internet site:
Be aware
After we discuss sitemaps within the context of search engine optimisation, we often imply XML sitemaps. Any further, we’ll discuss XML sitemaps on this information.
Handbook Verify
The best solution to discover an XML sitemap is to search for it manually. Mostly, an internet site’s XML sitemap can be situated at this URL handle: “https://area.com/sitemap.xml.”
Very often—particularly if the web site makes use of WordPress and the Yoast search engine optimisation plugin—you will be redirected to a sitemap index (/sitemap_index.xml).
In that case, it’ll appear to be this:
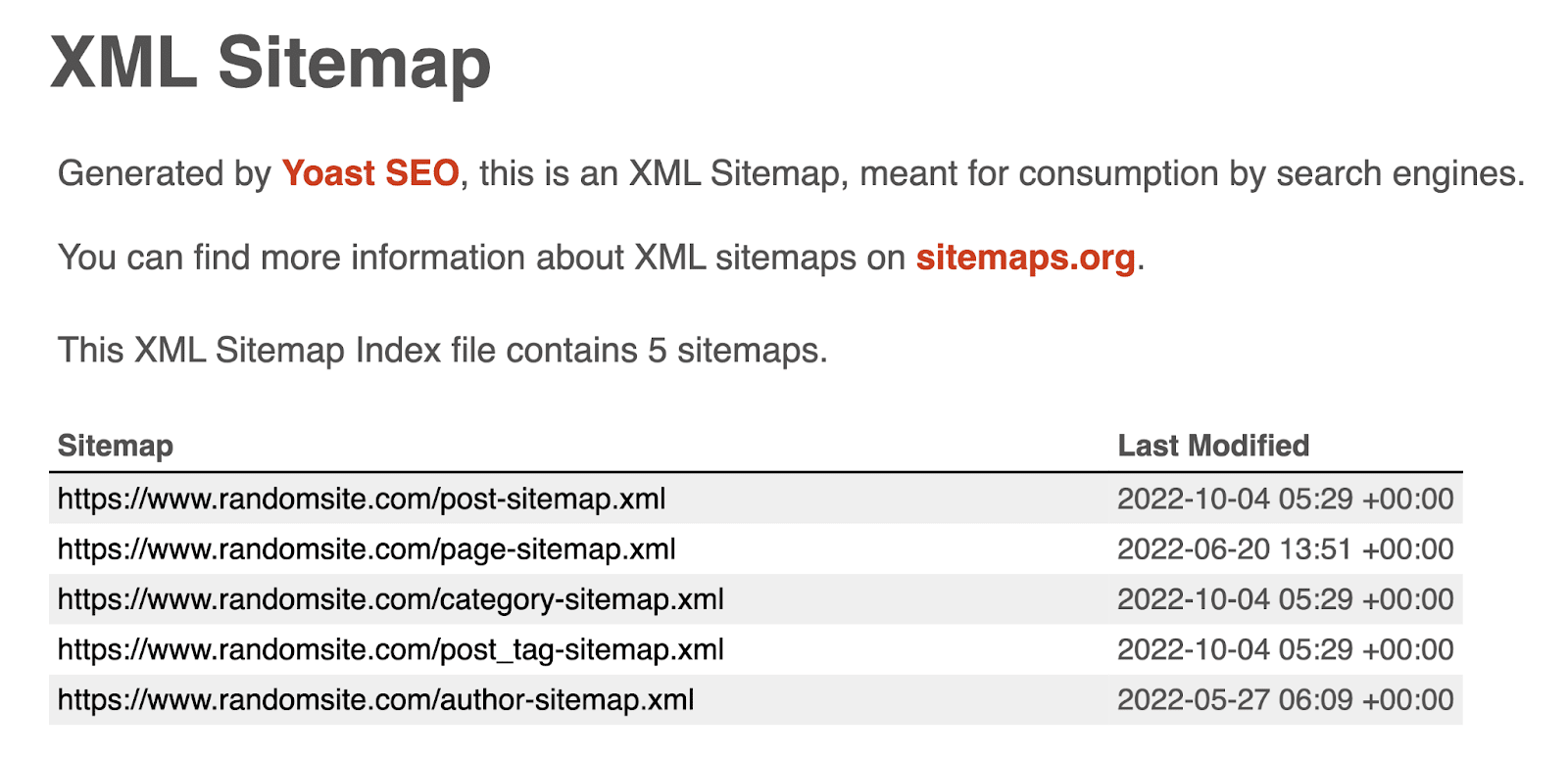
As you may see, a sitemap index is a straightforward file that lists all of the sitemaps an internet site has. (Sure, there may be a number of sitemaps.)
To see the precise sitemap, simply click on the hyperlink to the precise sitemap within the index.
Search Operators
Search operators are particular instructions you may add to go looking queries to return extra particular outcomes.
Listed below are some search operators you should utilize to discover a web site’s sitemap:
- “website:[domain.com] filetype:xml”
- “website:[domain.com] inurl:sitemap”
- “website:[domain.com] intitle:sitemap”
Merely enter the operator into the search bar and substitute “area.com” with the precise web site’s handle.
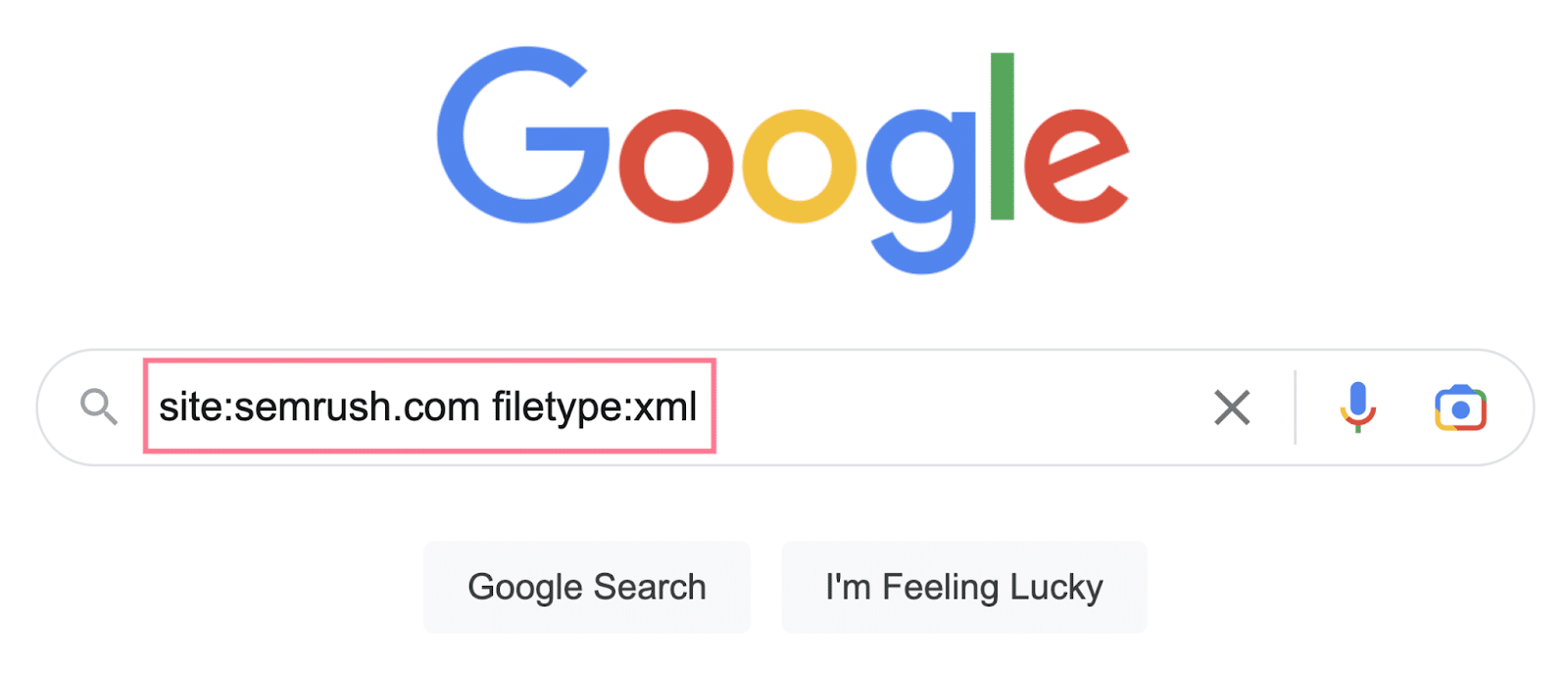
The search outcomes ought to return the placement of the web site sitemap—if it exists and the search engine you’re utilizing has listed it.
Google Search Console
When you’ve got entry to your web site’s Google Search Console (GSC), there’s an opportunity the sitemap has been submitted there.
Head to the “Sitemaps” report within the “Indexing” part of the left menu.
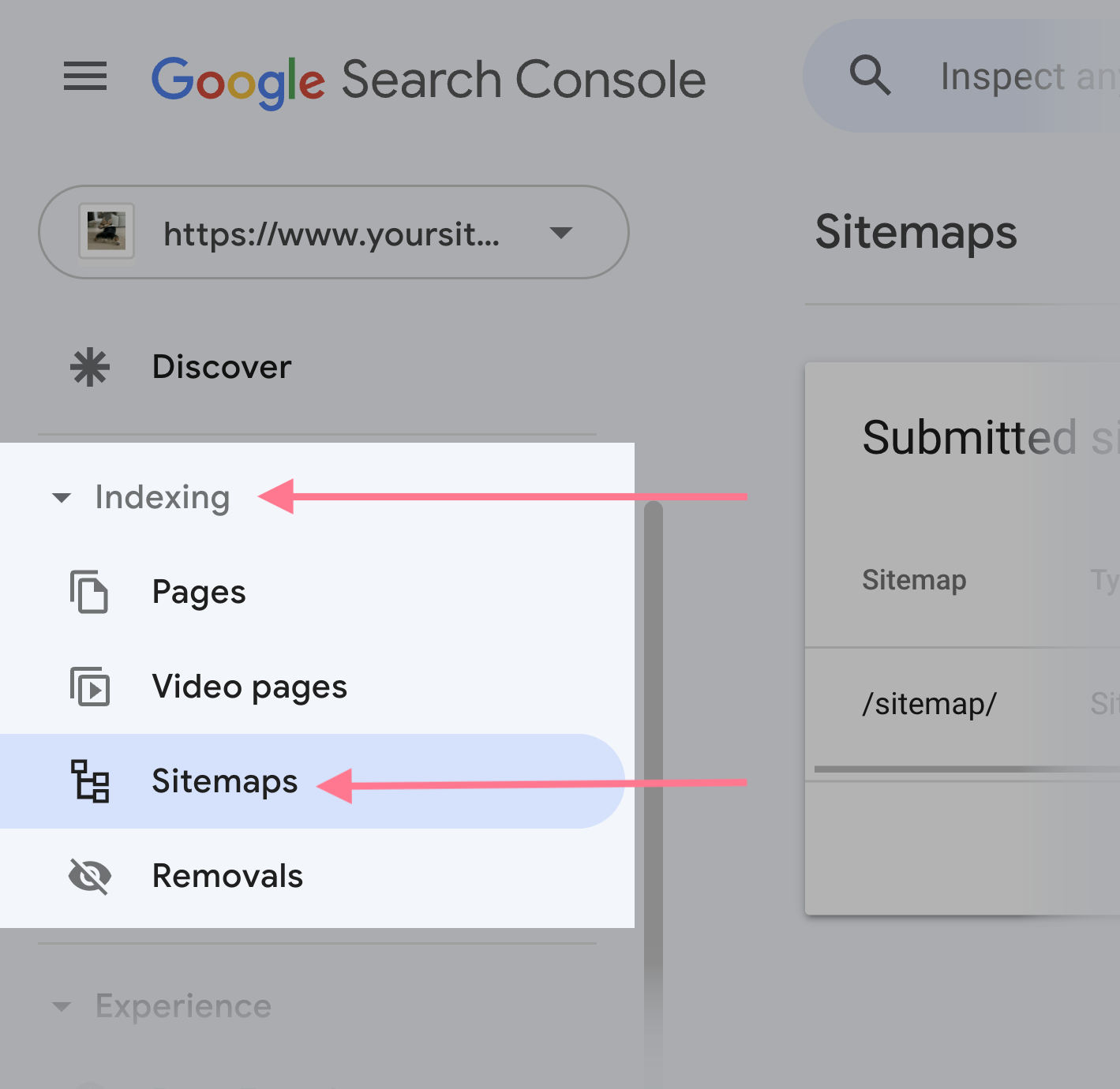
Right here, you will see a bit known as “Submitted sitemaps.”
If somebody has submitted an XML sitemap earlier than, you will discover its URL within the record.
Be aware
We’ll discuss submitting a sitemap to Google Search Console later on this information.
Robots.txt
A robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which sections of the web site they need to crawl and which they need to keep away from.
It ought to go within the root folder of your website: “https://area.com/robots.txt.”
If the robots.txt file follows finest practices, it’ll hyperlink to the web site sitemap. Simply seek for “sitemap” inside the robots.txt file.
The part linking to a sitemap will look one thing like this:

Tip
For those who’ve tried all of the methods talked about above and could not find your XML sitemap, your web site most likely would not have one. So, learn our information to XML sitemaps to discover ways to create one or use a sitemap generator.
How you can Evaluate Your Sitemap for Points
To make sure your sitemap is about up accurately, use Semrush’s Website Audit.
The device will crawl your web site (much like the best way Googlebot does) and detect any issues associated to your sitemap (if current). And also will test for different technical points in your website.
To start, add your homepage URL to the textual content bar. Then, click on “Begin Audit.”

Subsequent, select your settings for the audit.
Comply with our detailed setup information should you need assistance.
Subsequent, click on “Begin Website Audit.”
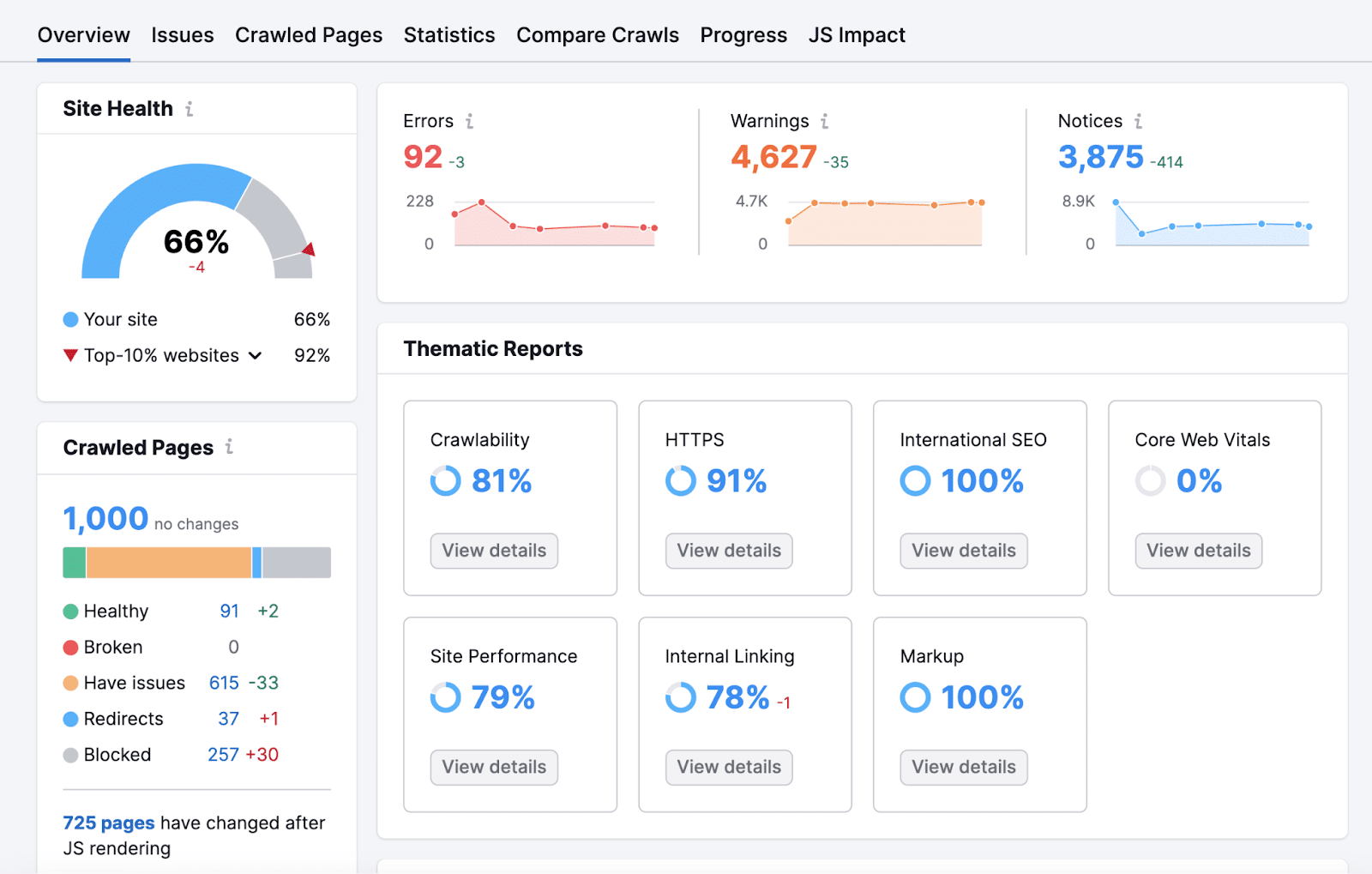
As soon as the audit is full, you’ll arrive on the device’s “Overview” report. Right here’s what it appears to be like like:
Click on the “Points” tab. Then, seek for “sitemap” within the textual content field.
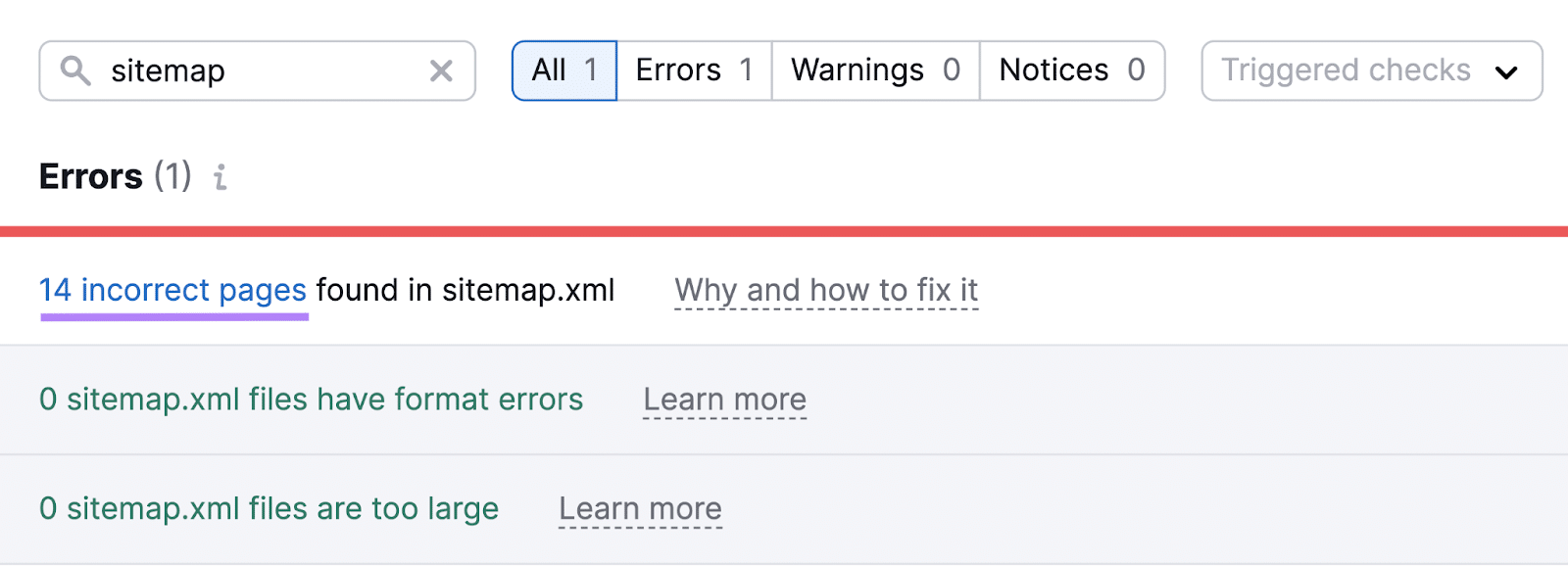
You may get an inventory of points associated to your sitemap.xml file.
Handle “Errors” first, then transfer on to “Warnings” and “Notices.”
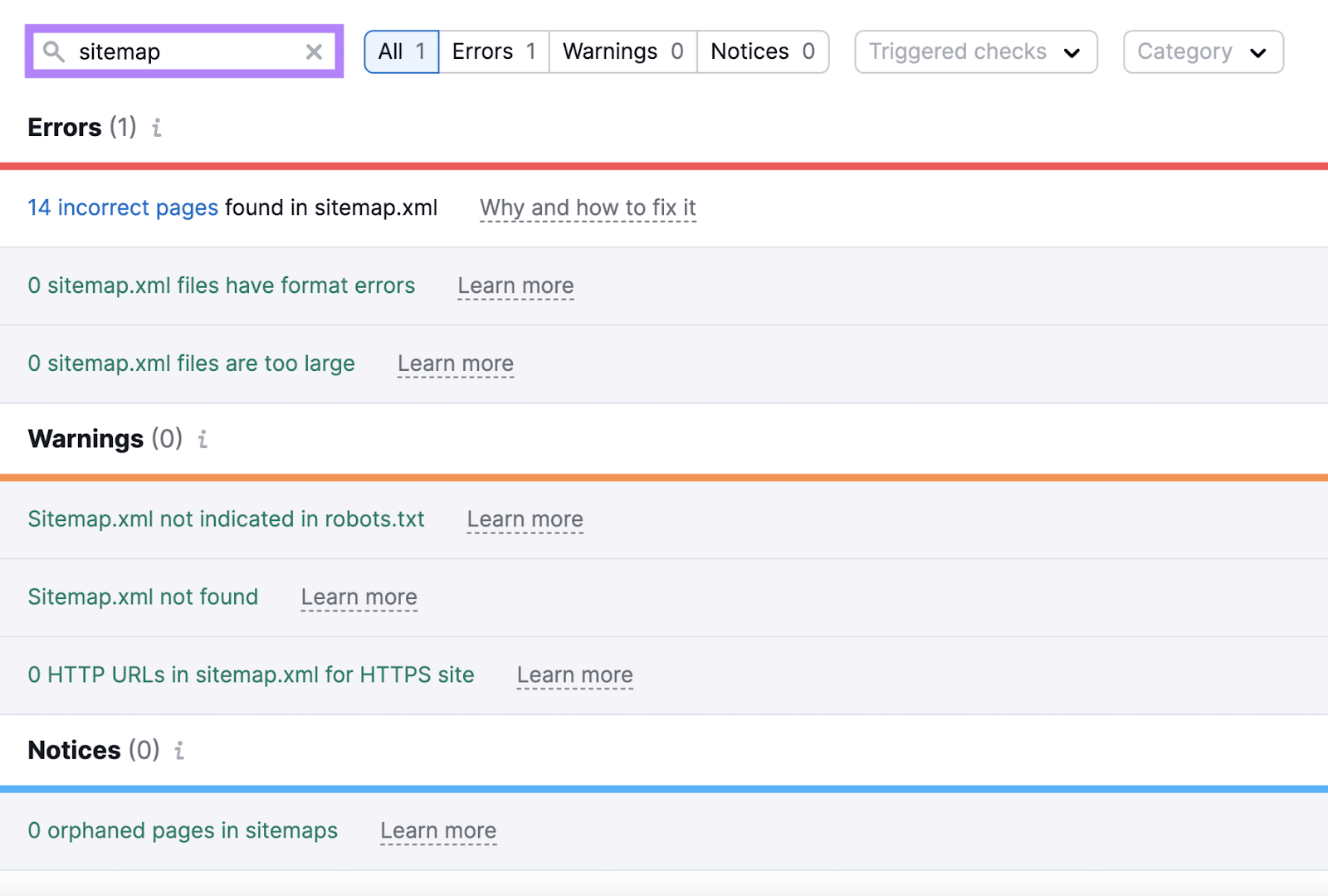
Some frequent sitemap-related points embrace:
- Sitemap has format errors: There are format errors (like lacking XML tags) in your sitemap file
- Incorrect pages present in a sitemap: Your sitemap comprises pages that aren’t alleged to be in a sitemap (like pages with redirects or pages that aren’t canonical variations)
- Sitemap information are too massive: Your sitemap exceeds Google’s measurement restrict (greater than 50MB or greater than 50,000 URLs)
- Sitemap not indicated in robots.txt: Your robots.txt file doesn’t point out the trail to your sitemap. Together with this path is a finest apply as a result of it directs serps to your sitemap. And facilitates sooner and extra full indexing.
- Sitemap not discovered: The sitemap URL offered returns a 404 error. This could possibly be as a consequence of a typo within the sitemap URL, the sitemap not being uploaded, or it being positioned within the flawed listing.
- HTTP URLs in sitemap for HTTPS website: Your sitemap comprises HTTP URLs on an HTTPS website. All URLs needs to be HTTPS to forestall duplicate content material points and safety warnings in browsers.
- Orphaned pages in sitemaps: These are pages which might be listed within the sitemap however don’t have any inner hyperlinks pointing to them from different pages on the location. This makes it arduous to search out them and may restrict these pages’ potential to rank nicely.
Click on one of many hyperlinks with the variety of affected pages to see a full record of pages with that particular challenge.
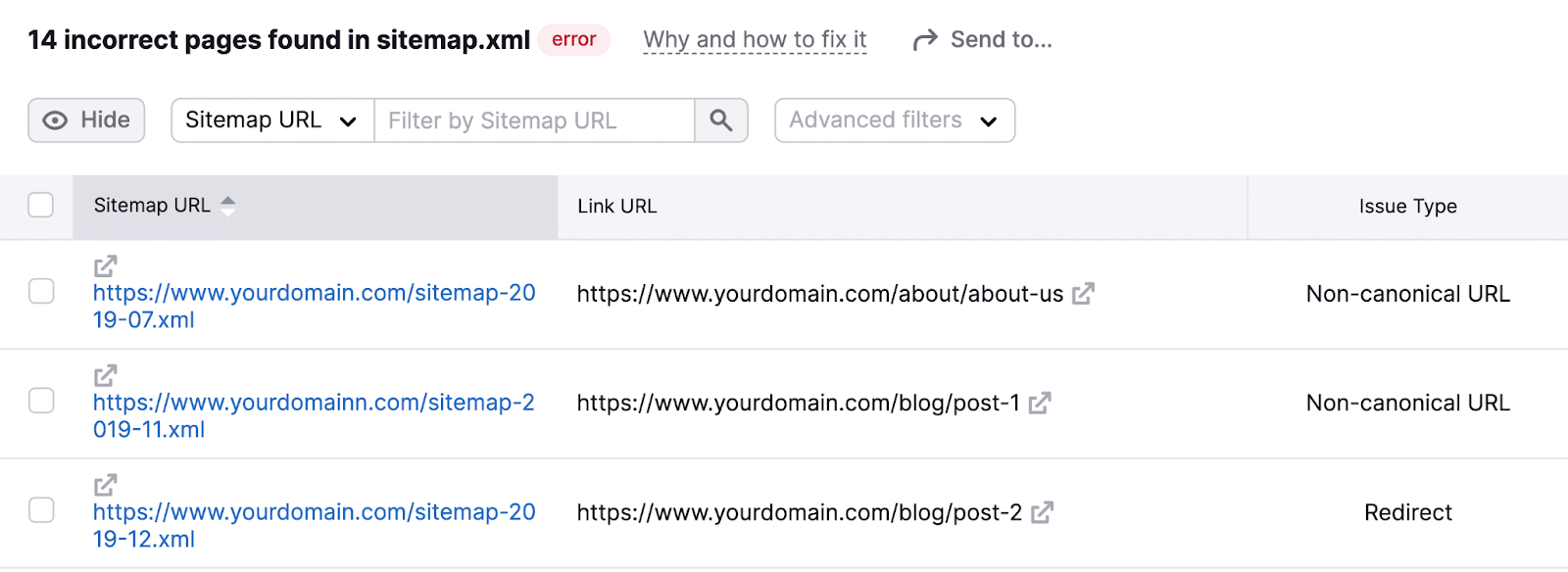
Subsequent, click on “Why and how you can repair it” subsequent to every kind of challenge.
This can open a window with a proof of the issue. And recommendations on how you can repair it.
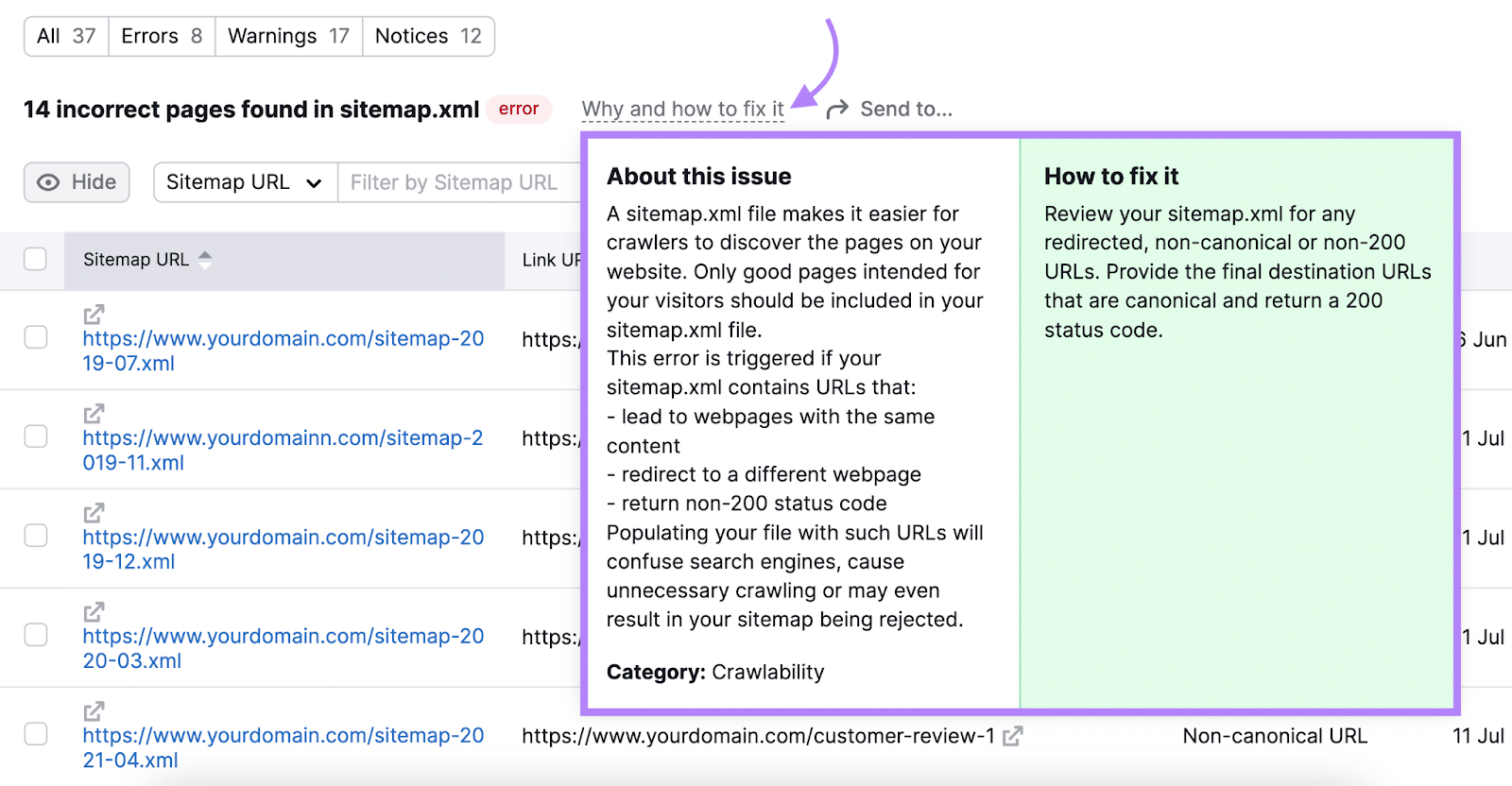
Undergo the record and implement the required adjustments.
Then, rerun the audit to substantiate that each one points have been efficiently resolved.
How you can Submit a Sitemap to Google
Submitting your XML sitemap to Google is an search engine optimisation finest apply.
Why?
- It might probably velocity up the method of Google discovering your sitemap
- It might probably provide help to detect points together with your sitemap
Submit your sitemap in Google Search Console. (If you do not have an account but, create one so you may log in to GSC.)
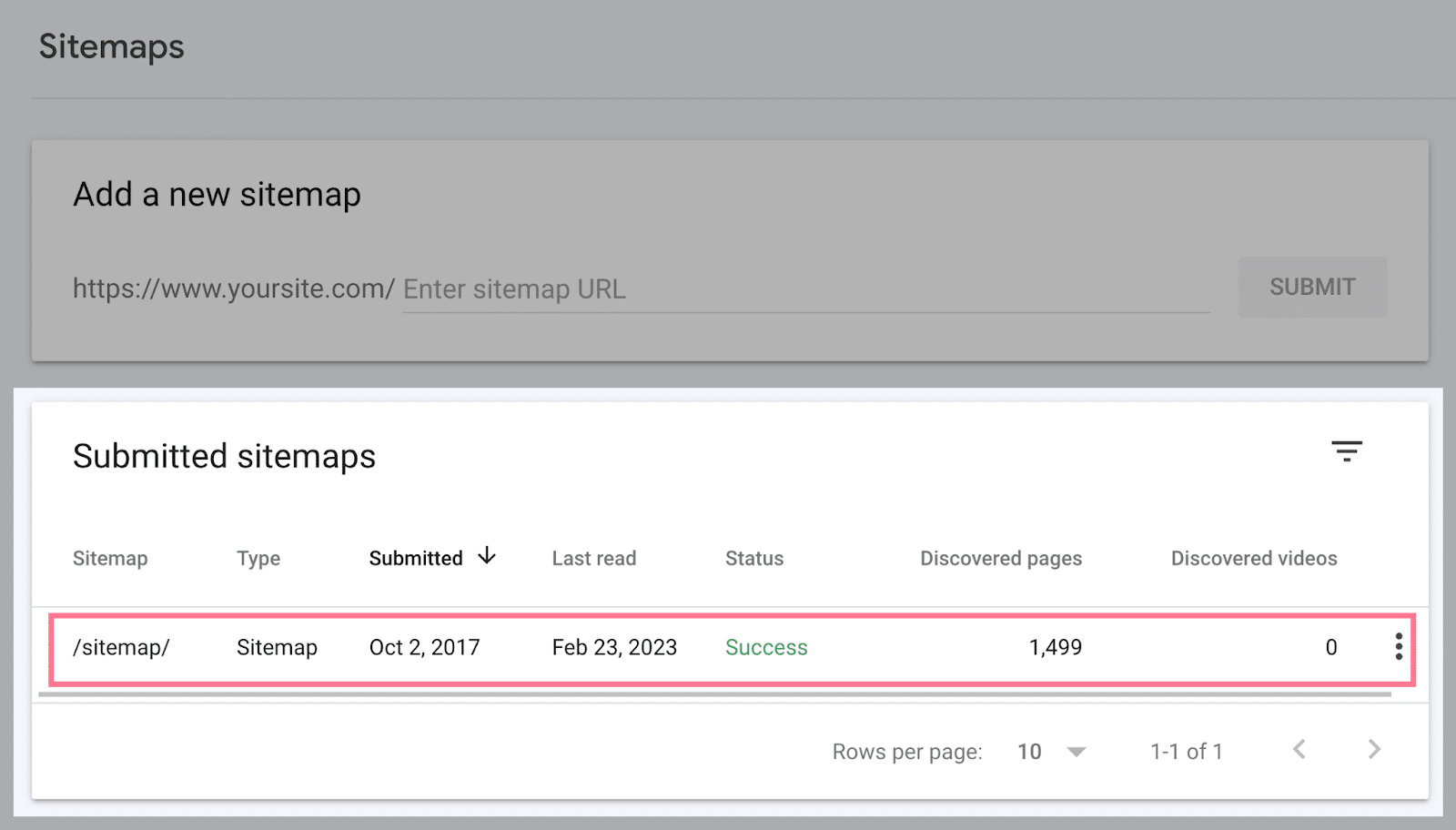
To submit your sitemap, go to the “Sitemaps” report. You may discover it within the “Indexing” part of the left menu.
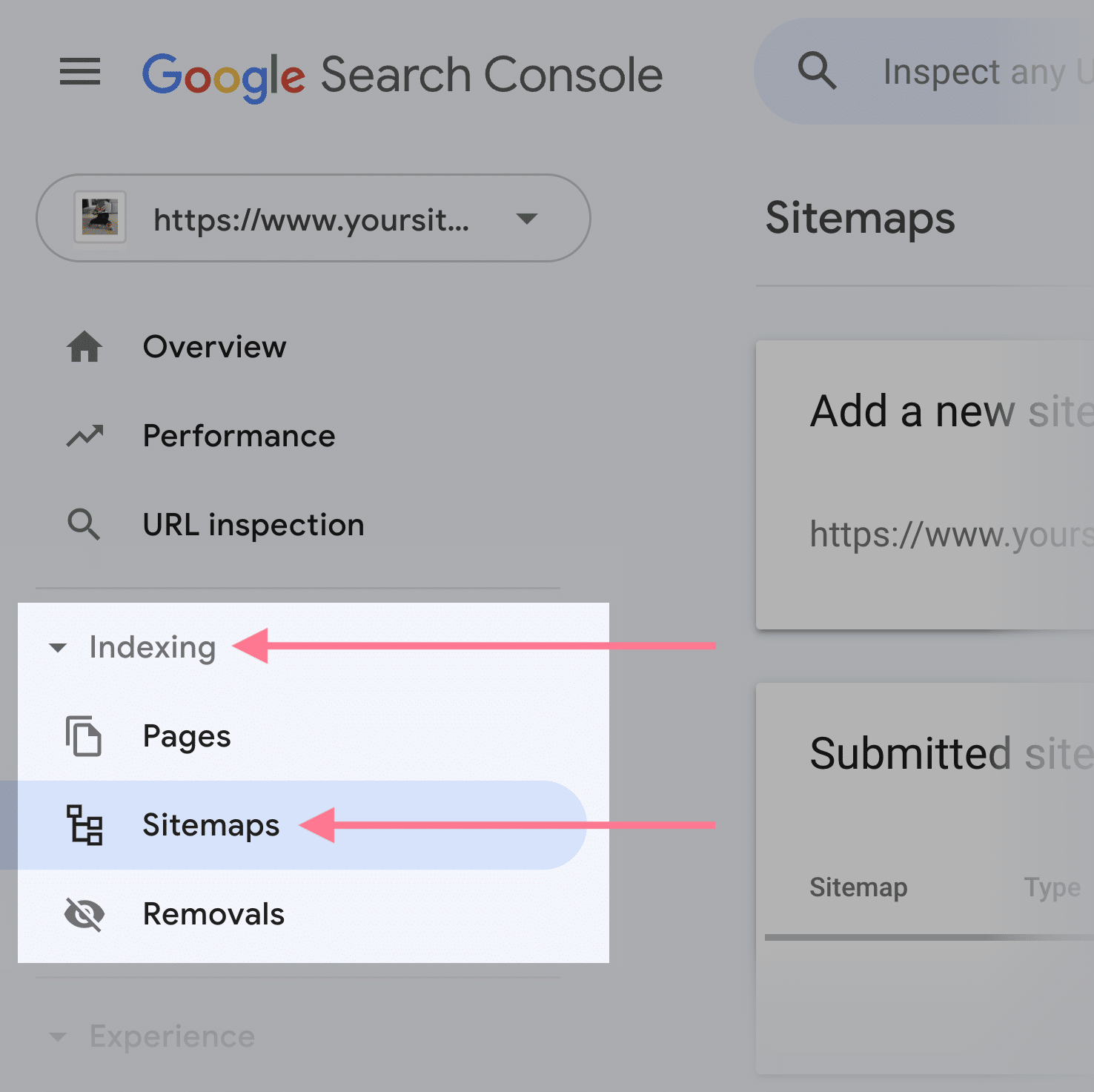
There, enter your XML sitemap’s URL within the “Add a brand new sitemap” part. And click on the “Submit” button.
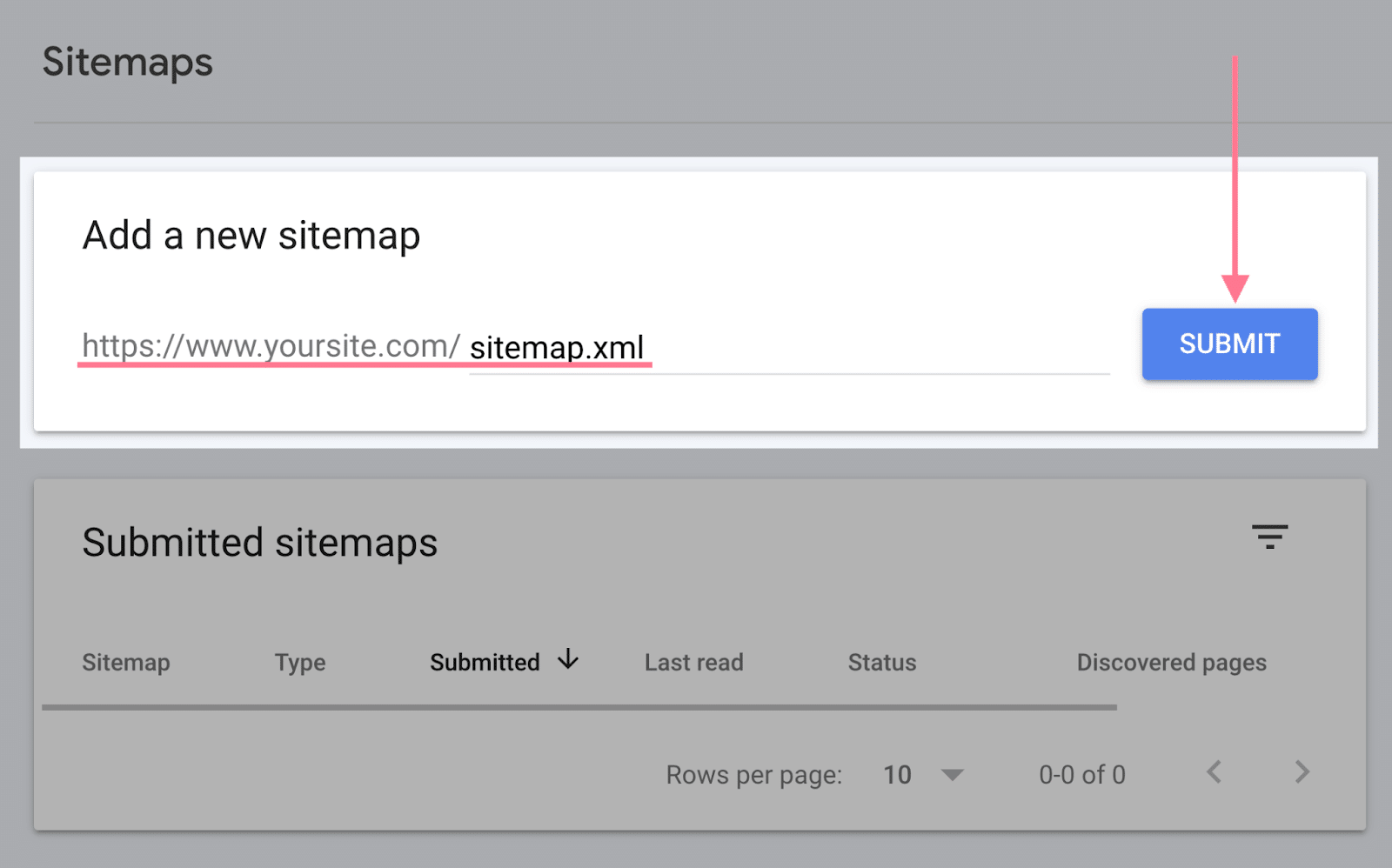
After you’ve got submitted your sitemap, you will get a message like this:
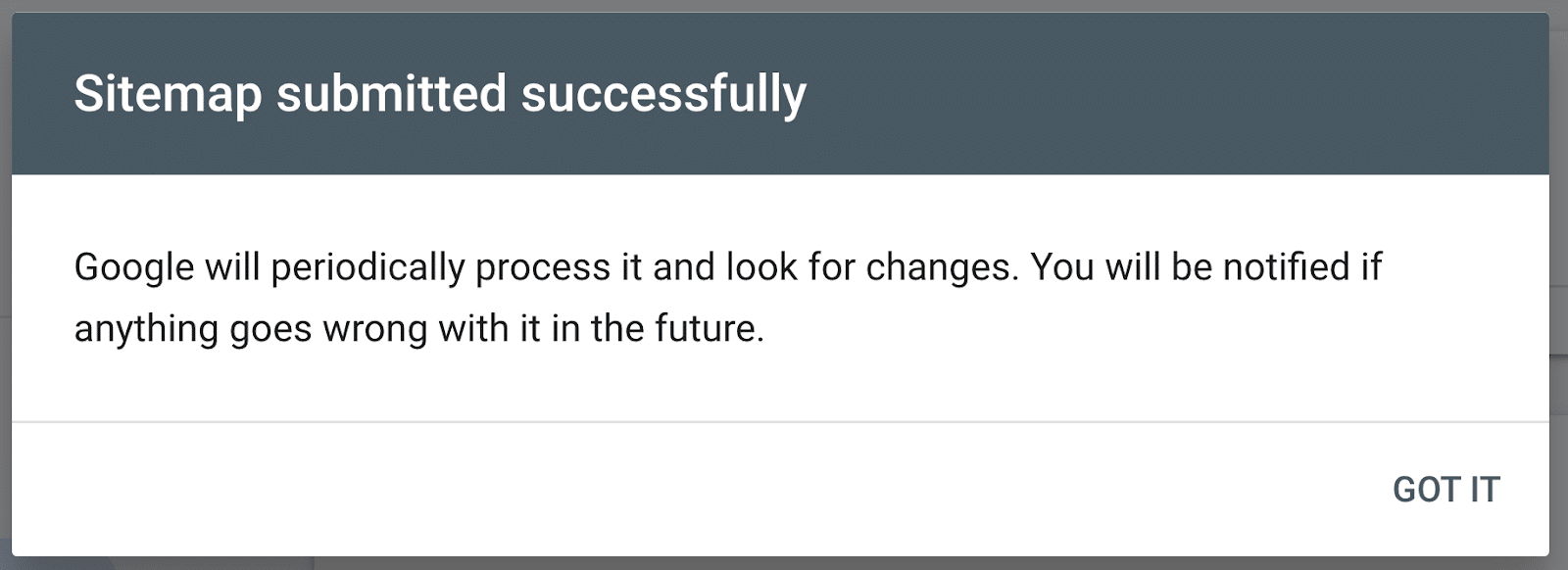
For a extra in-depth information, learn our submit on how you can submit a sitemap to Google.
Monitor the standing of your sitemap anytime you go to the report. If there is a inexperienced “Success” message, you are all good.
If there’s a difficulty together with your sitemap, you will see a purple “Could not fetch” or “Has errors” standing. On this case, the report will present an in depth clarification of what went flawed and how you can repair it.
Verify the complete record of doable errors and how you can repair them in Google’s information to the “Sitemaps” report.
FAQs
Beneath are some frequent questions associated to sitemaps. With solutions and extra sources.
Do I Want a Sitemap for a Small Web site?
Google states that web sites with 500 or fewer pages could not want a sitemap. However provided that the entire pages are correctly linked and discoverable by search engine crawlers.
That stated, there aren’t any downsides to having an XML sitemap. And in case your web site commonly updates content material for search engine optimisation functions, a sitemap can velocity up the method of Google discovering these adjustments.
What Shouldn’t Be Included in a Sitemap?
All the pages listed in your sitemap ought to present Google that your website is high-quality and well-maintained.
Meaning you need to pass over some pages. Resembling:
- Pages with 3xx, 4xx, or 5xx standing codes
- Orphaned pages
- Duplicate pages
- Pages that aren’t the canonical model
- Pages with a “noindex” robots tag
- Pages blocked in your robots.txt file
How Huge Is Too Huge for a Sitemap?
A single sitemap needs to be restricted to 50MB or 50,000 URLs.
Google encourages customers to comply with finest practices outlined by sitemaps.org.
If yours exceeds the dimensions limits, you’ll want to separate up your sitemap.
Then, create and submit a sitemap index file to Google. So it may possibly determine all your sitemaps.
How Usually Ought to You Generate a Sitemap?
The extra typically you replace and publish new content material, the extra typically you need to generate a sitemap.
As a normal rule, we advocate auditing your sitemap as soon as monthly. For those who publish a number of items of content material per day, it’s possible you’ll have to replace your sitemap on a weekly foundation.
Simply maintain an eye fixed out for errors. Which is simple with the Website Audit device.